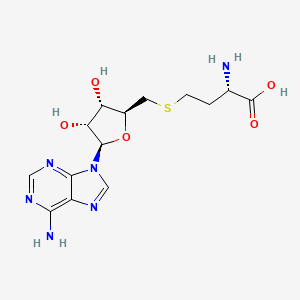
S-Adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH) is the biosynthetic precursor to homocysteine. SAH is formed by the demethylation of S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Adenosylhomocysteinase converts SAH into homocysteine and adenosine.
Biological role
DNA methyltransferases are inhibited by SAH. Two S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine cofactor products can bind the active site of DNA methyltransferase 3B and prevent the DNA duplex from binding to the active site, which inhibits DNA methylation.
References
External links
- BioCYC E.Coli K-12 Compound: S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine